记录基本的数据结构知识
单链表
常量和类型定义
-
C/C++
typedef struct LNode{ ElemType data; struct LNode* next; }LNode, *LinkList; Linklist L = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); -
Python
class LNode: def __init__(self, elem): self.data = elem self.next = None class LinkList: def __init__(self): self.head = LNode("头节点") # head是头指针,指向头结点,而头结点的data中不存储任何信息。 -
Java
一些题目
-
求带头结点的单链表长度。
int Length(LinkList L){ Node* p = L; int count = 0; while(p->next != NULL){ count++; p = p->next; } return count; }def Length(L): q = L.head count = 0 while q.next != None: count += 1 q = q.next return count -
用尽可能短的时间,将两个带头结点的单链表连接在一起。
void Connect(LinkList &ha, LinkList &hb, int m, int n, LinkList &hc){ // 将ha和hb指向的单链表合并,用hc传出来 Linklist hd; if(m<=n){ hc = ha; hd = hb; }// hc指向短的,hd指向长的 Node* p = hc; while(p->next != NULL){ p = p->next; } p->next = hd->next; free(hd); ha = NULL; hb = NULL; }def Connect(L1, m, L2, n, L3): ha = L1.head hb = L2.head if m > n: ha, hb = hb, ha p = ha while p.next != None: p = p.next p.next = hb.next L3.head = ha -
一个递增有序的带头结点的单链表,写一个高效算法,删除所有值相同的多余元素
void Purge(LinkList L){ if(L->next != NULL){ Node* p = L->next; while(p->next != NULL){ if (p->data == p->next->data){ q = p->next; p->next = q->next; free(q); }else{ p = p->next; } } } }def Delete(L): p = L.head q = p.next while p.next is not None: if q is not None: while q.data == p.data: q = q.next p.next = q p = p.next q = p.next -
单链表就地逆置
void Reverse(LinkList &L){ if(L->next!=NULL){ p = L->next; L->next = NULL; do{ q = p->next; p->next = L->next; L->next = q; }while(p!=NULL); } }def Reverse(L): p = L.head q = p.next p.next = None while q is not None: s = q.next q.next = p.next p.next = q q = s -
已知有一个指针指向单链表中的某个结点,以尽可能快的方式删除这个结点。
void Delete(Node* s, ElemType e){ e = s->data; s->data = s->next->data; s->next = s->next->next; }def Delete_one(L, s): s.data = s.next.data s.next = s.next.next -
编写递归算法,求单链表长度(无头结点)
int Length(LinkList L){ if(L==NULL){ return 0; }else{ return Length(L->next) + 1; } }def Length(L): if L is None: return 0 else: return 1 + Length(L.next) -
编写递归算法,释放单链表的空间(无头结点)
void free(LinkList &L){ if (L!=NULL){ Delete(L->next); free(L); L = NULL; } } -
编写递归算法,逆序输出单链表(无头结点)
void Write(LinkList L){ if(L != NULL){ Write(L->next); printf(L->data); } }def Write(L): if L is not None: Write(L.next) print(L.data, end=" ") -
编写递归算法,判断单链表中是否有元素的值和位序相等的元素(无头结点)
void Exsist(LinkList L, int position){ if (L==NULL){ return False; }else if(L->data == position){ return True; }else{ return Exsist(L->next, position+1); } }def Exsist(L, position): if L is None: return False elif L.data == position: return True else: return Exsist(L.next, position+1)
树
常量和类型定义
typedef struct BiNode{
ElemType data;
struct BiNode* lchild;
struct BiNode* rchild;
}BiNode, *BiTree;
typedef struc CSNode{
ElemType data;
struct CSNode* firstchild;
struct CSNode* nextsibling;
}CSNode, *CSTree;
创建和生成二叉树
-
从控制台输入生成二叉树
- 不是先、中、后、层序创建,而是一种类似层序的,从上到下,从左到右的创建过程。具体是:从根开始a开始,创左子树b,再创b的左子树,如果b的左子树为空,返回空,再接着创建b的右子树。图解如下:
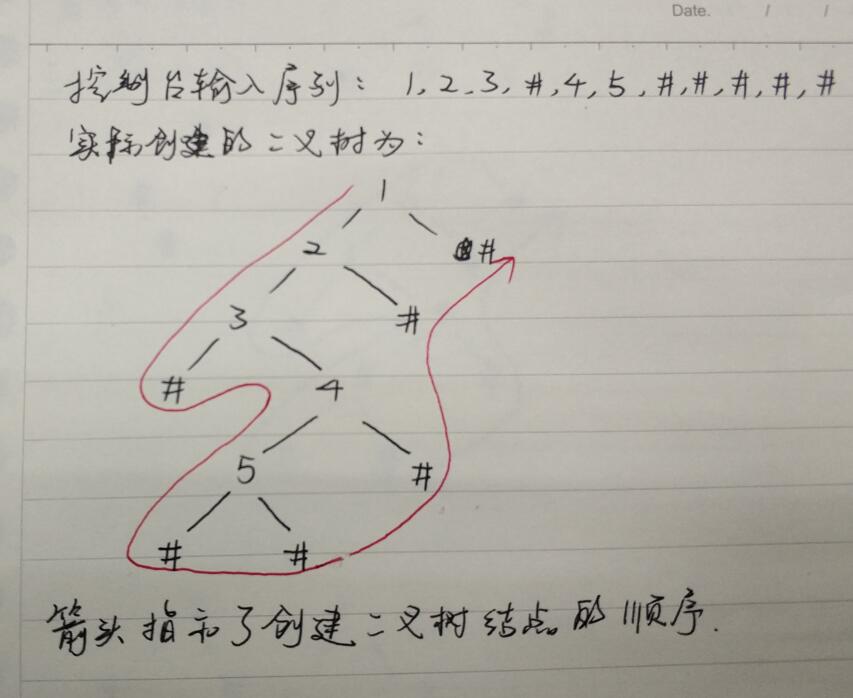
void create_BiTree(BiTree *T) { char ch; scanf("%d",&ch); if(ch=='#') *T = NULL; else { *T = (BiNode *)malloc(sizeof(BiNode)); if(!T) { printf("开辟内存失败\n"); exit(1); } (*T)->data = ch; creatBT(&(*T)->lchild); creatBT(&(*T)->rchild); } }def create_BiTree(bt=None): x = input() if x is "#": bt = None else: bt = BiNode(x) bt.lchild = createBiTree(bt.lchild) bt.rchild = createBiTree(bt.rchild) return bt -
根据一个层序序列的列表创建二叉树,相对于上一种方法,更直观一些。
def create_BiTree2(T, lst, i): if i < len(lst): if lst[i] == '#': return None else: T = BiNode(lst[i]) T.lchild = create_BiTree2(T.lchild, lst, 2*i+1) T.rchild = create_BiTree2(T.rchild, lst, 2*i+2) return T return T
一些题目
-
二叉树不是树的特例
-
二叉树的五种基本形态
-
二叉树的中序序列(树的后根序列) + 任一个其他序列 唯一确定一个二叉树或树
- 先序:根左右
- 中序:左根右
- 后序:左右根
- 逆中序:右根左
- 逆后序:根右左
- 树的后根序列即对应二叉树的中序序列
-
递归遍历二叉树
void PreOrder(BiTree T){ visit(*T); PreOrder(T->lchild); PreOrder(T->rchild); }def PreOrder(T): if T is not None: print(T.data, end=" ") PreOrder(T.lchild) PreOrder(T.rchild) -
非递归先序遍历二叉树
void PreOrder(BiTree T){ InitStack(s); Push(s, NULL); p=T while(p!=NULL){ while(p!=NULL){ visit(*T); if(p->rchild!=NULL){ Push(s, p); } p = p->lchild; } Pop(s, p); } }def PreOrder2(T): S = [] S.append(None) p = T while p is not None: while p is not None: print(p.data, end=" ") if p.rchild is not None: S.append(p.rchild) p = p.lchild p = S.pop() -
删除子树,释放占用的空间
void Delete(BiTree &T){ if(T!=NULL){ Delete(T->lchild); Delete(T->rchild); free(T); T=NULL; } } -
判断两棵二叉树是否相似/镜像/相等
Status Similar(BiTree T1, BiTree T2){ if (T1==NULL && T2==NULL){ return True; }else if(T1==NULL && T2!=NULL){ return False; }else if(T1!=NULL && T2==NULL){ return False; }else{ return Similar(T1->lchild, T2->lchild) && Similar(T1->rchild, T2->rchild); } }def Similar(T1, T2): if T1 is None and T2 is None: return True elif T1 is None or T2 is None: return False else: return Similar(T1.lchild, T2.lchild) and Similar(T1.rchild, T2.rchild) -
交换一个二叉树的左右子树
void Swap(BiTree T){ Swap(T->lchild); Swap(T->rchild); temp = T->lchild; T->lchild = T->rchild; T->rchild = temp; }def Swap(T): if T is not None: Swap(T.lchild) Swap(T.rchild) T.lchild, T.rchild = T.rchild, T.lchild -
求一个二叉树的高度(利用二叉树的五种形态)
int Depth(BiTree T){ if(T==NULL){ return 0; }else{ return 1 + max(Depth(T->lchild), Depth(T->rchild)); } }def Height(T): if T is None: return 0 else: return 1 + max(Height(T.lchild), Height(T.rchild)) -
求一个二叉树的高度(利用带一个参数遍历的方法)
void Depth(BiTree T, int level, int &d){ if(T!=NULL){ if(level > d){ d = level; } Depth(T->lchild, level+1, d); Depth(T->rchild, level+1, d); } }def Depth(T, level, lst): if T is not None: if level > lst[0]: lst[0] = level Depth(T.lchild, level+1, lst) Depth(T.rchild, level+1, lst) -
求二叉树度为0的结点(叶子结点)个数
int Count(BiTree T){ if(T==NULL){ return 0; }else if(T->lchild==NULL && T->rchild==NULL){ return 1; }else{ return Count(T->lchild) + Count(T->rchild); } }def Count(T): if T is None: return 0 elif T.lchild is None and T.rchild is None: return 1 else: return Count(T.lchild) + Count(T.rchild) -
求二叉树度为1的结点
int Count(BiTree T){ if (T==NULL){ return 0; }else if(T->lchild!=NULL && T->rchild==NULL){ return 1 + Count(T->lchild); }else if(T->lchild==NULL && T->rchild!=NULL){ return 1 + Count(T->rchild); }else{ return Count(T->lchild) + Count(T->rchild); } }def Count2(T): if T is None: return 0 elif T.lchild is None and T.rchild is not None: return 1 elif T.lchild is not None and T.rchild is None: return 1 else: return Count2(T.lchild) + Count2(T.rchild) -
将一棵二叉树根朝左,躺倒打印出来(见严蔚敏习题集)
- 逆中序遍历次序决定行数
- 结点所在的层数决定列数
void Print(BiTree T, int level){ if(T!=NULL){ Write(T->rchild, level+1); for(int i=0; i<level; i++){ printf(" "); } printf(T->data); printf("\n"); Write(T->lchild, level+1); } }def Write(T, level): if T is not None: Write(T.rchild, level+1) for i in range(level): print(" ", end="") print(T.data) Write(T.lchild, level+1) -
统计一棵由孩子兄弟链表表示的树中,叶子的个数
即统计没有firstchild的结点个数
int Count(CSTree T){ if(T==NULL){ return 0; }else if(T->firstChild==NULL){ return 1 + Count(T->nextsibling); }else{ return Count(T->firstchild) + Count(T->nextsibling); } }def Count3(T): if T is None: return 0 elif T.lchild is None: return 1 + Count3(T.rchild) else: return Count3(T.lchild) + Count3(T.rchild) -
统计一棵由孩子兄弟链表表示的树,树的度为多少
即统计↘方向的结点个数
void Count(CSTree T, int &d){ if(T!=NULL){ p = T->firstchild; if(p != NULL){ n = 1; while(p!-=NULL){ n++; p=p->next; } if(n > d){ d = n; } } Count(T->lchild, d); Count(T->rchild, d); } } -
求树/森林的深度
int Depth(CSTree T){ if(T==NULL){ return 0; }else{ return max(1 +Depth(T->firstchild), Depth(T->nextsibling)); } } -
判断一棵二叉树是否中序有序(判断一个二叉排序树是否合法)
Status BST(BiTree T, BiTree &pre){ // pre指向被访问的结点的中序前驱 if (T==NULL){ return True; }else{ if(BST(T->lchild, pre) == False){ return False; } if(pre != NULL && T->data <= pre.data){ return False; } pre = T; return BST(T->rchild, pre); } }# 用一个全局变量pre def BST(T): global pre if pre is not None: print(pre.data) if T is None: return True else: if not BST(T.lchild): return False if pre is not None and T.data < pre.data: return False pre = T return BST(T.rchild) # 用一个引用型变量pre_lst def BST2(T, pre_lst): if T is None: return True else: if not BST2(T.lchild, pre_lst): return False if pre_lst[0] is not None and T.data < pre_lst[0].data: return False pre_lst[0] = T return BST2(T.rchild, pre_lst) -
将一个结点插入一个二叉排序树
void InsertBST(BiTree &T, BiNode* p){ if(T==NULL){ T = p; }else if(p->data < T->data){ InsertBST(T->lchildb, p); }else if(p->data > T->data){ InsertBST(T->rchild, p); }else{ free(p); } }
图
常量和类型定义
邻接表存储表示
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct ArcNode{
int adjvex;
struct ArcNode* nextarc;
}ArcNode;
typedef struct VNode{
Elemtype data;
ArcNode* firstarc;
}VNode;
typedef struct Graph{
Graph[MAX_SIZE] vertices;
int vexnum, arcnum;
}
class ArcNode:
def __init__(self, adjvex, nextarc, weight):
self.adjvex = adjvex # 这条边指向谁
self.nextarc = nextarc # 下一条边是哪个
self.weight = weight # 边的权值
class VNode:
def __init__(self, index, data, firstarc):
self.index = index # 顶点的编号
self.data = data # 顶点的数据
self.firstarc = firstarc # 指向第一条边
class Graph:
def __init__(self, vertices, vexnum, arcnum):
self.vertices = vertices # VNode组成的列表
self.vexnum = vexnum # 顶点数
self.arcnum = arcnum # 边数
class ArcNode{
int weight; // 边的权重
int vexIndex; // 这条边指向的节点 的编号
ArcNode nextArc; // 下一条边
ArcNode(int weight, int adjVex, ArcNode nextArc){
this.weight = weight;
this.vexIndex = vexIndex;
this.nextArc = nextArc;
}
}
class VNode{
int index; // 节点的编号
String data; // 节点的数据
ArcNode firstArc; // 从这个点出发的第一条边
VNode(int index, String data, ArcNode firstArc){
this.index = index;
this.data = data;
this.firstArc = firstArc;
}
}
class Graph{
int vexNum;
int arcNum;
VNode[] vertices;
Graph(int vexNum, int arcNum, VNode[] vertices){
this.vexNum = vexNum;
this.arcNum = arcNum;
this.vertices = vertices;
}
}
一些题目
- 采用深度优先遍历的方法,判断是否存在从i号结点到j号结点的路径
Status DFS(Graph G, int i, int j, Status visited[], Status &found){
ArcNode *p;
visisted[i] = True;
if(i==j){
found = True;
}else{
p = G.vertices[i].firstarc;
while(!found && p!=NULL){
if(!visited[p->adjvex]){
DFS(G, p->adjvex, j, visited, found);
}
p = p->nextarc;
}
}
}
Status Path(Graph G, int i, int j){
Status visited[MAx_SIZE];
Status found;
for(int k=0; k<G.vexnum; k++){
visited[k] = False;
}
found = False;
DFS(G, i, j, visited, found);
return found;
}
def dfs(G, i, j, visited, found):
visited[i] = True
if i == j:
found[0] = True
else:
p = G.vertices[i].firstarc
while not found[0] and p is not None:
if not visited[p.adjvex]:
dfs(G, p.adjvex, j, visited, found)
p = p.nextarc
def path(G, i, j):
visited = [False for i in range(G.vexnum)]
found= [False]
dfs(G, i, j, visited, found)
return found[0]
if __name__ == "__main__":
INF = float('inf')
adj = [[0,8,INF,5,INF], # 先用邻接表表示
[INF,0,3,INF,INF],
[INF,INF,0,INF,6],
[INF,INF,9,0,INF],
[INF,INF,INF,INF,0]]
# 将邻接表表示的图存储在邻接链表里
vertices = []
vexnum = len(adj)
for i in range(len(adj)): # 初始化顶点列表
vertices.append(VNode(i, "顶点"+str(i)+"的data", None))
arcnum = 0
for i in range(len(vertices)):
v = vertices[i]
p = None
for j in range(len(adj[v.index])):
weight = adj[i][j]
if 0 < weight < INF:
arcnum += 1
if p is not None:
p.nextarc = ArcNode(j, None, weight)
else:
p = ArcNode(j, None, weight)
vertices[i].firstarc = p
G = Graph(vertices, vexnum, arcnum)
print(G.vexnum)
print(G.arcnum)
print(path(G, 0, 4))
print(path(G, 1, 3))